Improving the Focus of the Eye With Cataract Surgery
Intraocular Lens Implants
During cataract surgery, the cloudy lens, or cataract, is replaced by a man-made lens implant. The eye is measured beforehand in order to determine the implant power required to provide the best focus of the eye. Depending on individual preference, a focus for near or far can be chosen. Placement of a monofocal lens implant is a routine part of the cataract procedure, and is covered by OHIP. The lens implant is permanent — it will never wear out, and cannot get rejected.
Certain specialty lenses are also available. These include the following:
- Aspheric Monofocal Lens: This lens is designed to minimize distortion of light rays as they enter the eye, thus improving a quality of vision known as contrast sensitivity. The improvement is most noticeable in low light conditions, for example during night driving or walking around in your home at night.
- Multifocal Lens: This lens style is designed to significantly reduce dependence on glasses by providing distance, intermediate and near vision. Common side effects may include haloes around bright point sources of light and glare with night driving.
- Extended Depth of Focus Lens: This lens gives a wider range of vision than with the aspheric lens and significantly reduces dependence on glasses.
- Toric Lens: This lens improves the focus of the eye when it is not round, but rather football-shaped.
Not all individuals will be candidates for specialty lenses. If a lens is an option for you, you will be given information about it at the time of your surgical consultation with Dr. Misra. It is important to remember that there is no medical reason to have any one of these lenses: they are technological advances that may be chosen based on each individual’s preferences and lifestyle.
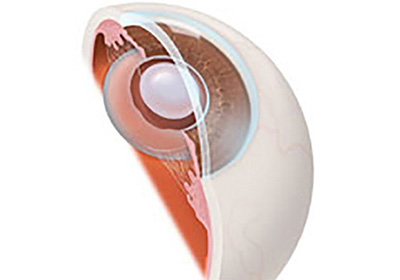
Lens implant in place.

Lens implant.
Improving The Focus of the Eye When It Is Not Round
What is astigmatism?
Astigmatism is an anatomic condition that some individuals are born with. It means that the clear windshield at the front of the eye, the cornea, is shaped more like a football than a soccer ball. As a result, light and visual images do not come to a focus at a single point, but rather at two or more points, causing the vision to be blurry and out of focus.
What can be done about astigmatism and what are PCRIs?
Astigmatism can be compensated for with glasses and contact lenses. It can be significantly reduced and in some cases eliminated by peripheral corneal relaxing incisions (PCRIs) and laser vision correction. With PCRIs, incisions are placed along the steep part of the cornea to modify its shape and make it more spherical.
A special type of lens implant, known as a toric lens implant, can also be placed in the eye to correct astigmatism. Correction by toric lens is more durable than with PCRI.
What are the benefits of having PCRIs placed?
Patients that undergo the PCRI procedure can expect increased clarity of vision even when not wearing glasses. In no case will PCRIs eliminate the need for reading glasses.
How does it feel to have the procedure done?
The PCRI procedure is performed at the time of cataract surgery. Having it done will not noticeably increase the length of time that is takes to complete the surgery and will not cause increased pain either during or after the surgery. At most, some patients notice a slightly gritty sensation in their eye as it heals after surgery. This is also the case for many patients having cataract surgery alone.
What if I don’t have the procedure done?
Patients that choose not to have the procedure done can sharpen their vision with a stronger prescription in their glasses.
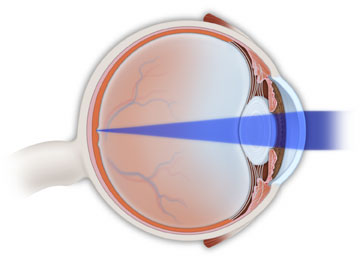
Eye without astigmatism.
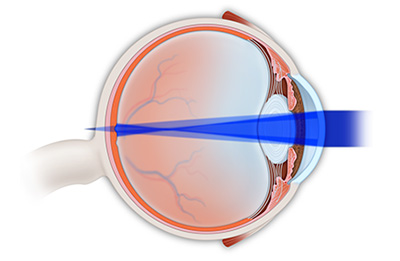
Eye with astigmatism.
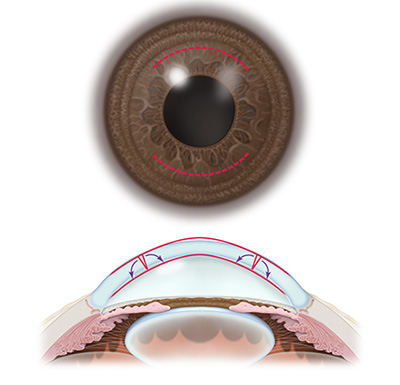
Eye with peripheral corneal relaxing incision.
